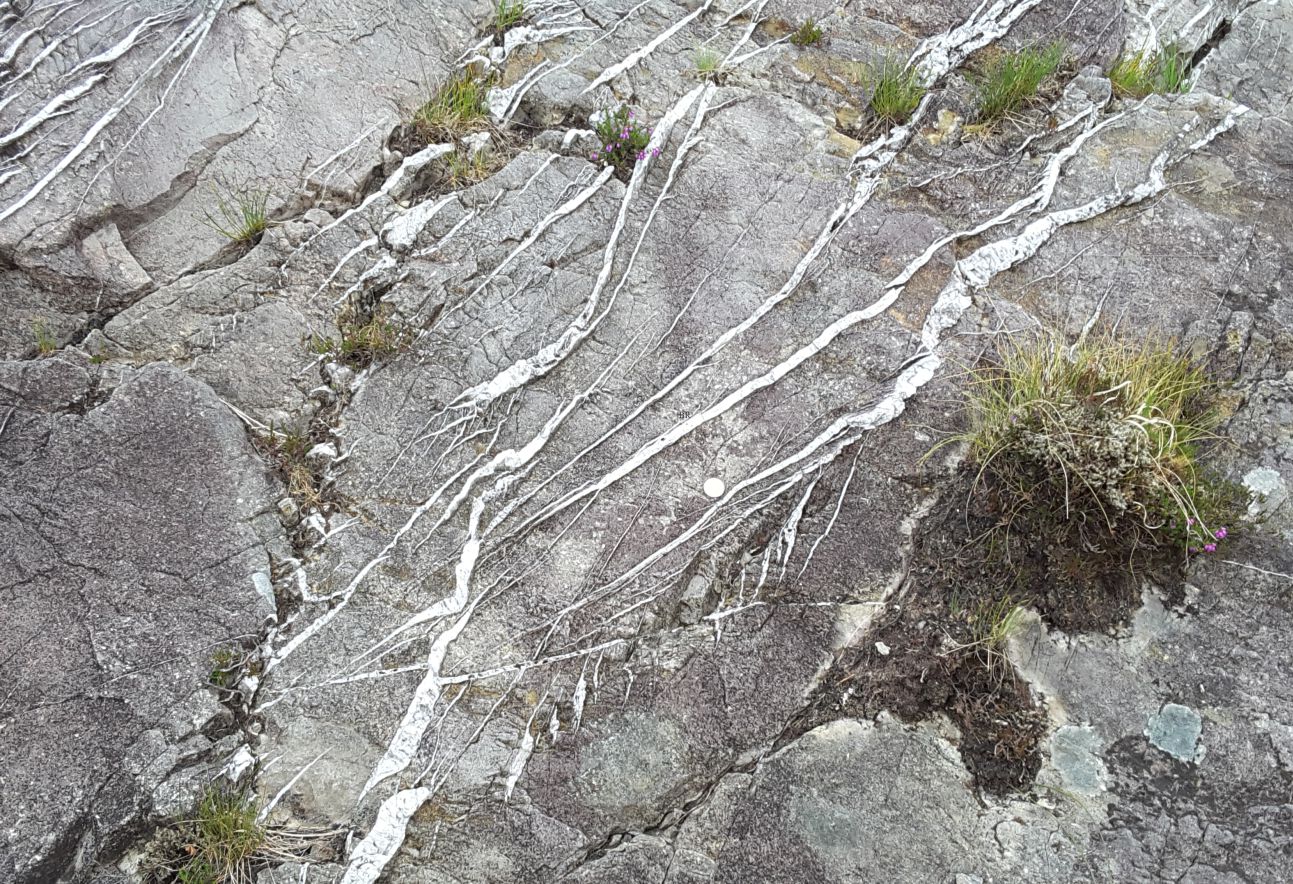
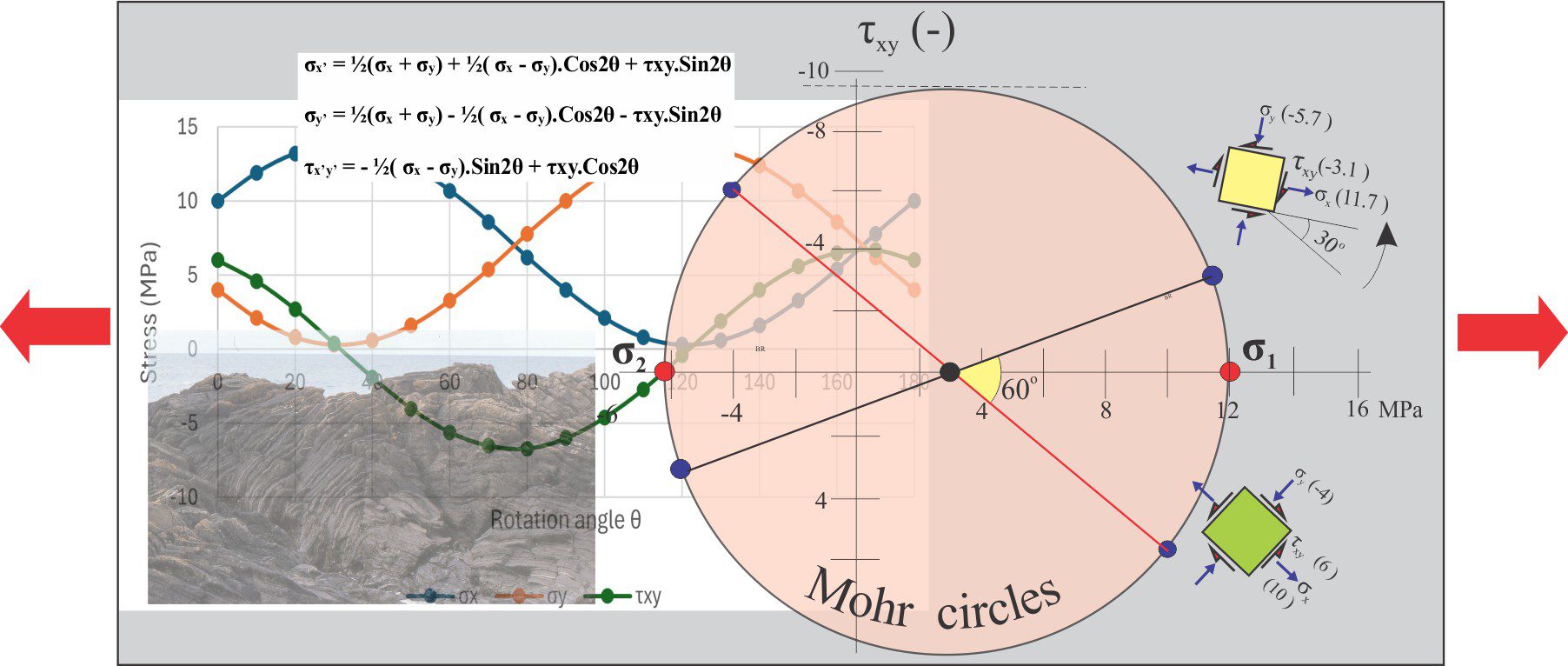
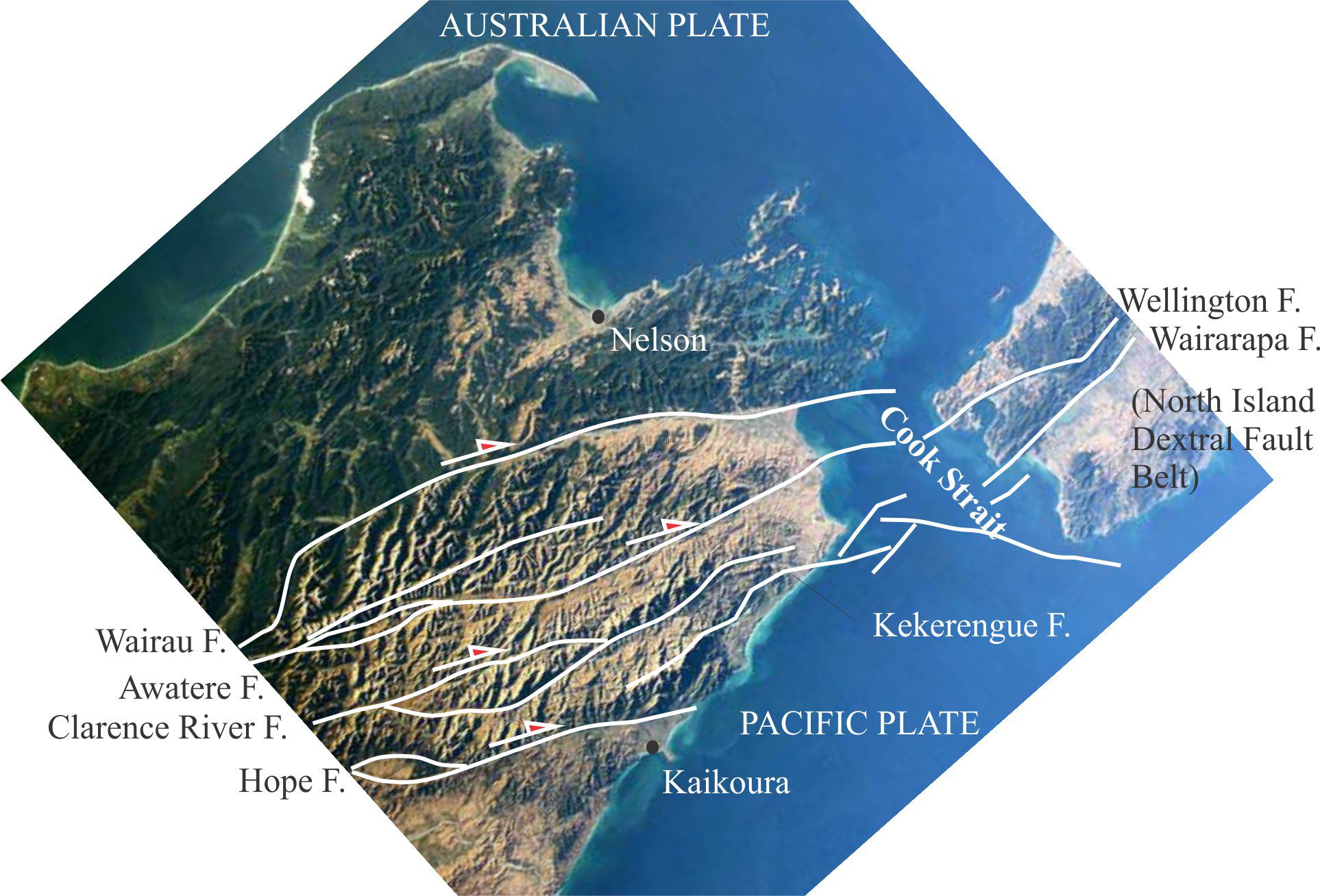
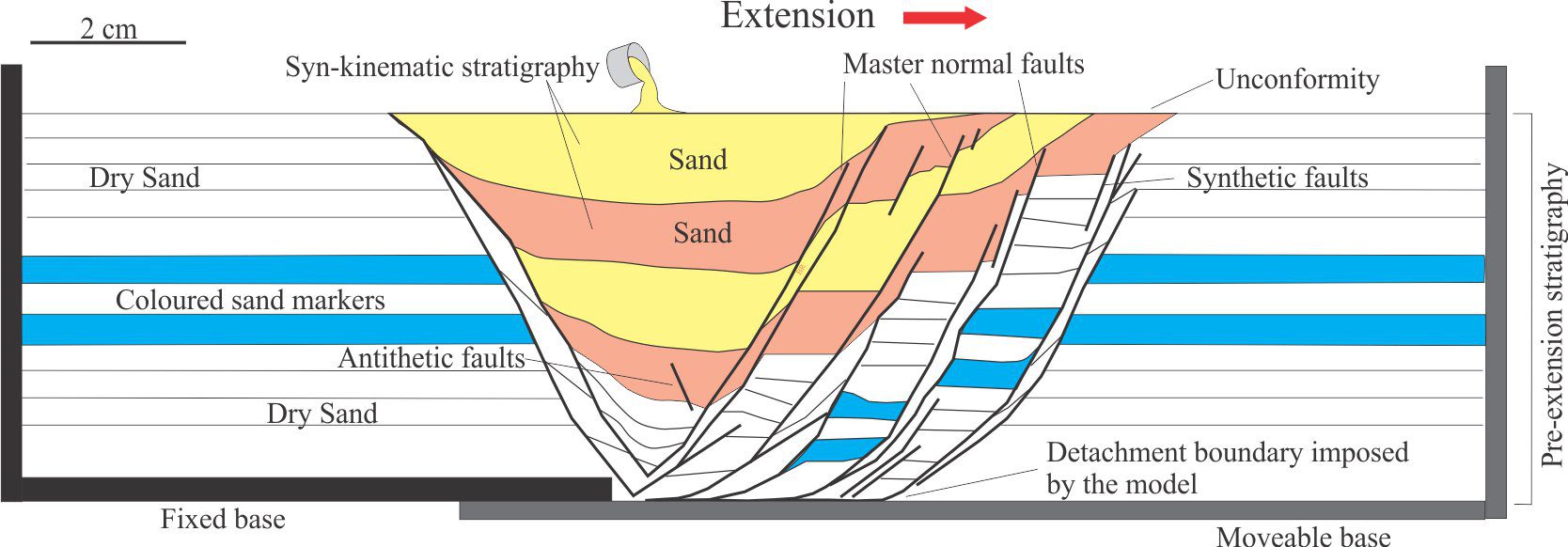
Girls into Geoscience A STEM networking group based at University of Plymouth; also Twitter
Nanogirl Live – Kids, STEM
K12 program, US Schools
Curious Minds – citizen science projects in NZ
NZ science learning resources
GNS Teaching resources, Scicomm
CSIRO education – outreach
British Geological Survey Scicomm, resources
National Science Foundation (US) teaching resources
Geology.com teaching earth science
National Science Teachers’ Association (USA)
NARST: A Worldwide Organization for Improving Science Teaching and Learning Through Research
Earth Science Teachers’ Association
Teaching Science in the Garden
Digital Encyclopedia of Ancient Life – images of fossils etc.
Sally Ride EarthKAM and Space Camp Students can request views and images from space of places they are interested in, around the world. This is a NASA mission.
The Earth Science Teachers Association (UK) Twitter