Here’s a selection of photos from the Burrens of County Clare, Ireland. Carboniferous limestones, in a glacio-karst landscape: karst structures, landscapes, vegetation, and fossils, from inland and shoreline exposures.
There is an article on the Burrens here.
This link will take you to an explanation of the Atlas series, the ownership, use and acknowledgment of images. There, you will also find links to the other Atlas categories.
Click on the image for an expanded view, then ‘back page’ arrow to return to the Atlas.
New Quay and Abott Hill:
Burrens landscape north of Boston (a few km south of New Quay. Limited soil cover on the limestone bedrock, and scrubby vegetation. Typical rounded hills of limestone in the background.
Views north of the estuary and Galway Bay from Abott Hill (between New Quay and Kinvara)
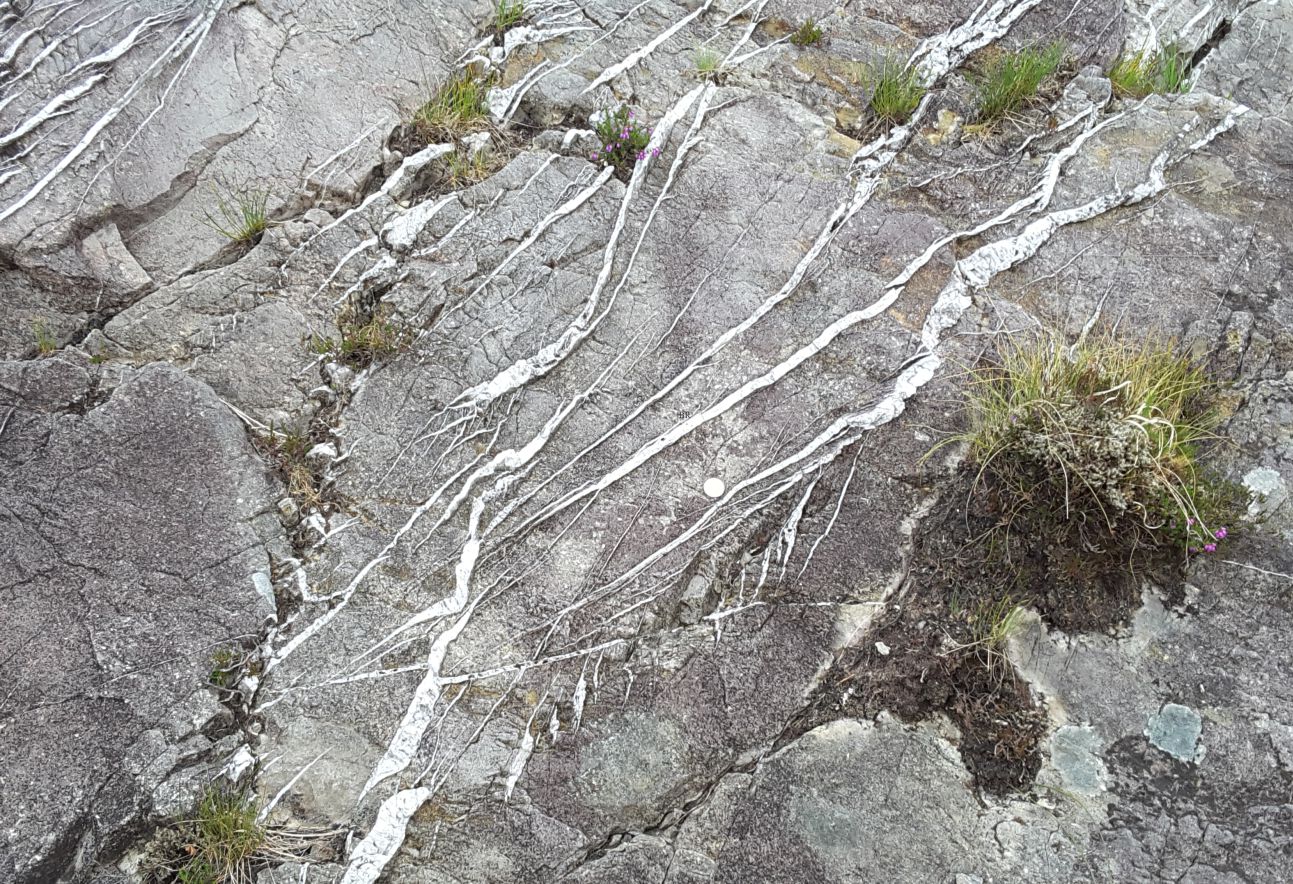
Clints and grykes, Abott Hill, typical Burren karst structures. Right image: smaller scale dissolution rills.
Typical Burren hill and more fertile lowland valley near New Quay
Flaggy Shore (near New Quay):
Salt corrosion and erosion of limestone along Flaggy Shore, has modified the clints and grykes. Some erosion is caused by potholed cobbles.
Clints and grykes on the raised shore platform along Flaggy Shore
Abundant colonial Visean corals, best seen on semi-polished surfaces along the Shore. These views are oblique and cross-sections of coral columns.
Black Head:
The raised shore platform at Black Head (below the road) consists of several benches elevated during post-glacial rebound.
Clints and grykes, typical karst structures, are well developed all over the Black Head platform, controlled by dominant fracture trends. They provide succor and shelter to a variety of small shrubs and wild flowers.
Smaller scale dissolution limestone rills are common along exposed gryke walls
Polished limestone along the Black Head shore reveal fossil corals and brachiopods. The stepped landforms are controlled by dominant fracture trends.
Tidal pools, regularly flushed by incoming tides.
Bouldery storm ridges have been pushed over the Black Head platform by Atlantic storms.
Typical vegetation eking out a living in the grykes. Succulents (left) are most common close to the shore.